10 Common Foot Problems and Treatments
Here are some of the most common foot ailments and what your podiatrist can do to treat them.
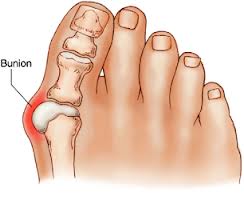
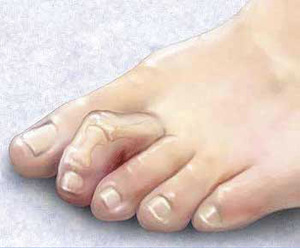
WHAT IS A BUNION?
WHAT IS A BUNION?
Definition:
A bunion is an enlargement at the base of the big toe caused by misalignment of the joint. It may be swollen, tender and painful with the wearing of footwear.
Causes:
Heredity, biomechanical abnormalities, neuromuscular disorders, inflammatory joint disease (arthritis), trauma, congenital deformities.
What might a podiatrist do?
Perform a physical exam of the foot, apply padding or taping and prescribe orthotics.
Recommend you have an X-ray evaluation through your G.P. who may refer you for surgery.
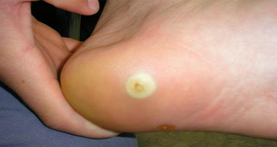
WHAT ARE CORNS OR CALLUSES?
Definition:
A callus or corn is a build up of skin that forms at points of pressure or over boney prominences. Calluses form on the bottom side of the foot, corns form on the top of the foot and between the toes.
Causes:
Repeated friction and pressure from skin rubbing against boney areas or against an irregularity in a shoe, as well as hereditary disorders.
What might a podiatrist do?
Perform a physical examination, perform trimming or padding of the lesions as needed.
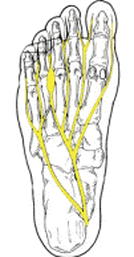
WHAT IS A NEUROMA?
A callus or corn is a build up of skin that forms at points of pressure or over boney prominences. Calluses form on the bottom side of the foot, corns form on the top of the foot and between the toes.
Causes:
Repeated friction and pressure from skin rubbing against boney areas or against an irregularity in a shoe, as well as hereditary disorders.
What might a podiatrist do?
Perform a physical examination, perform trimming or padding of the lesions as needed.
WHAT IS A NEUROMA?
Definition:
A neuroma is a painful condition often referred to as a pinched nerve, swollen nerve, or nerve tumor. It is defined more specifically as a benign growth of nerve tissue frequently found between the third and fourth toes. This may result in pain, burning, tingling, or numbness between the toes and in the ball of the foot.
Causes:
Improper or ill-fitting shoes, trauma, high heeled shoes, heredity.
What might a podiatrist do?
A physical examination, padding and taping, custom orthotics, and inflammatory medication.
GP referral for scan giving definite diagnosis to rule out other causes and refer for cortisone injections or surgery as needed.
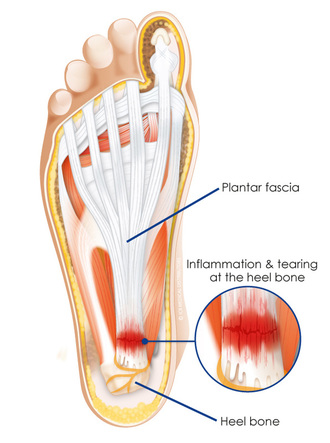
WHAT IS PLANTAR FASCIITIS / HEEL PAIN?
Definition:
Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the long band of connective tissue running from the heel to the ball of the foot, heel spur syndrome is a boney overgrowth on the heel bone, Plantar fasciitis and heel spur syndrome affect women more than men, The bottom of the foot and arch can become more painful.
Causes:
Stretching the long band of tissue that connects the heel and the ball of the foot, muscle imbalance, bone deformity, obesity, trauma, tightness of the muscles on the back of the leg.
What might a podiatrist do?
Perform a physical examination, recommend taping, ice treatment (using medical cool pack), prescribe orthotic devices, prescribe appropriate medication. Advice on supportive footwear.
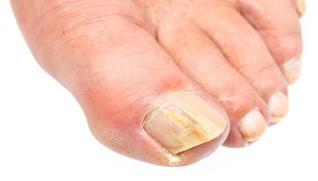
WHAT IS A FUNGAL NAIL?
Definition:
Nail Fungus is a chronic condition with implications for patients that go beyond the nail. When left untreated a fungal nail condition may affect physical and psychological wellbeing for many years. While not life threatening, the overall affects of this infection elevate its status to that of an important medical disorder.
Fungal nail is an infection: patients with a fungal nail condition may present nail discoloration, nail thickening, scaling, and/or detachment of the nail plate from the nail bed. Although, the cosmetic aspect of a fungal nail may be a concern, the problems induced may go much deeper.
More than 50% of patients with fungal nail experience pain and discomfort
A study on quality of life found significantly poorer ratings for general health and body pain in patients with fungal nail than in healthy subjects.
What might a podiatrist do?
When a fungal nail is diagnosed it should be treated with appropriate drug regimens to achieve a cure whether topically (cream, soaks, or nail lacquer) for the mild to moderate conditions and orally for moderate to severe nail conditions. Your podiatrist will choose the proper treatment for you.
WHAT IS ATHLETE'S FOOT?
Definition:
Athlete's foot is a common infection of the skin characterized by itching, scaling, redness, and the formation of small blisters. In general these lesions start between the toes and can extend to the borders and bottom of the foot. The fungus has the potential to spread to the toenails, causing them to become thickened, discolored and painful. In this case the infection is called onychomycosis. While this infection is common among athletes, keep in mind that can affect athletes and non-athletes alike.
Causes
The feet are vulnerable because shoes commonly create a warm, dark and humid environment that encourages fungal growth. Athletes foot can also be contracted in dressing rooms, hotel and locker room showers and swimming pool locker rooms where bare feet may come in contact with the fungus.
What Can You Do?
Keep shoes and socks dry as a preventive measure. Practice good foot hygiene including daily washing of the feet with soap and water; drying feet carefully, especially between the toes. Alternate shoes and change socks regularly (cotton socks).
What might a podiatrist do?
The podiatrist will give advice and recommend topical anti-fungal medication or refer to GP for oral anti-fungal medication.
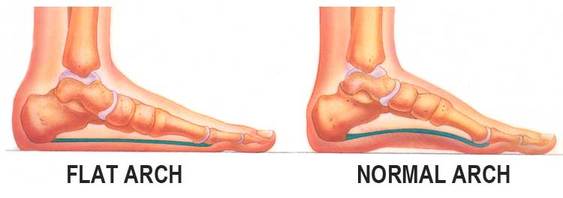
WHAT IS A FLAT FOOT / FALLEN ARCHES?
Definition:
A flat foot is a structural deformity resulting in the lowering of the arch of the foot. This is usually due tohyperpronation. In layman’s terms we refer to this as fallen arches. A person with a flat foot or a highly arched foot that is fairly painful is in need of treatment. People with flat feet may have other foot related problems such as ankle, knee, hip or lower back pain.
Causes
The main causes of flat feet or fallen arches are, heredity, arthritis, trauma, musculoskeletal disorders.
What Can You Do?
Wear supportive shoes.
What might a podiatrist do?
The podiatrist will perform a physical examination and gait analysis, take X-rays and prescribe customorthotics. Surgical options include an extensive flat foot reconstruction procedure or the use of a sinus tarsi titanium implant ie: HyProCure.
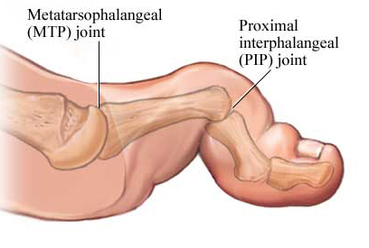
WHAT IS A HAMMER TOE?
.
Definition:
A hammer toe is a contraction deformity, resulting in a boney prominence on top of or in between the toes of the feet.
Causes
Hammer toe can be caused by: improper, ill-fitting or high heel shoes, trauma or heredity.
What Can You Do?
Change to shoes with lower heels, wear supportive shoes with a roomy toe box (width and depth).
Use of a cold compress to reduce inflammation.
What might a podiatrist do?
A podiatrist will perform a physical examination. Recommend padding and taping and recommend orthotics.
The podiatrist may also refer you to your GP for anti-inflammatory medication or cortisone injections.
For more information on hammertoes, mallet toes and claw toes click here
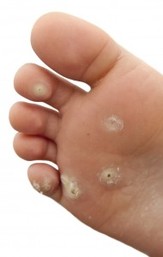
WHAT ARE WARTS (VERRUCAE/PLANTAR WART)?
Definition:
A hammer toe is a contraction deformity, resulting in a boney prominence on top of or in between the toes of the feet.
Causes
Hammer toe can be caused by: improper, ill-fitting or high heel shoes, trauma or heredity.
What Can You Do?
Change to shoes with lower heels, wear supportive shoes with a roomy toe box (width and depth).
Use of a cold compress to reduce inflammation.
What might a podiatrist do?
A podiatrist will perform a physical examination. Recommend padding and taping and recommend orthotics.
The podiatrist may also refer you to your GP for anti-inflammatory medication or cortisone injections.
For more information on hammertoes, mallet toes and claw toes click here
WHAT ARE WARTS (VERRUCAE/PLANTAR WART)?
Definition:
Warts are one of several soft tissue condition of the foot that can be quite painful. They are caused by a virus, which generally invades the skin through small or invisible cuts and abrasions. They can appear anywhere on the skin, but, technically, only those on the sole are properly called plantar warts/verrucae.
Children, especially teenagers, are often more susceptible to warts than adults; some people seem to be immune.
Problems
Most warts/verrucae are harmless, even though they may be painful. They are often mistaken for corns or calluses – which are layers of dead skin that build up to protect an area which is being continuously irritated. It is wise to consult a podiatrist when any suspicious growth or eruption is detected on the skin of the foot in order to ensure a correct diagnosis. Verrucae/plantar warts tend to be hard and flat with a rough surface and well-defined boundaries; warts are generally raised and fleshier when they appear on the top of the foot or on the toes. Plantar warts are often gray or brown (but the color may vary), with a center that appears as one or more pinpoints of black. It is important to note that warts can be very resistant to treatment and have tendency to reoccur.
Sources Of Virus
The causative virus thrives in warm, moist environments, making infection a common occurrence in communal bathing facilities (we recommend using bathing footwear e.g. flip-flops. If left untreated, warts can grow to an inch or more in circumference and can spread into clusters of several warts; these are often called mosaic warts. Like any other infectious lesion, plantar warts are spread by touching, scratching, or even by contact with skin shed from another wart. The wart may also bleed - another route for spreading. Occasionally, warts can spontaneously disappear after a short time, and, just as frequently, they can recur in the same location. When plantar warts develop on the weight-bearing areas of the foot – the ball of the foot, or the heel, for example – they can be the source of sharp, burning pain. Pain occurs when weight is brought to bear directly on the wart, although pressure on the side of a wart can create equally intense pain.
What can you do?
• Avoid walking barefoot, except on the sandy beaches.
• Change shoes and socks daily.
• Keep feet clean and dry.
• Check children’s feet periodically.
• Avoid direct contact with warts — from other persons or from other parts of the body.
• Do not ignore growths on, or changes in, your skin.
• Visit your podiatrist as part of your annual health checkup.
Self treatment is generally not advisable. Over-the-counter preparations contain acids or chemicals that destroy skin cells, and it takes an expert to destroy abnormal skin cells (warts) without also destroying surrounding healthy tissue.
Self treatment with such medications especially should be avoided by people with diabetes and those with cardiovascular or circulatory disorders. NEVER use them in the presence of an active infection.
What Might The Podiatrist Do?
Podiatrists may prescribe, supervise your use of a wart-removal preparation and treat pain symptoms.
We also are able to refer you to a GP for minor Cryotherapy treatment.
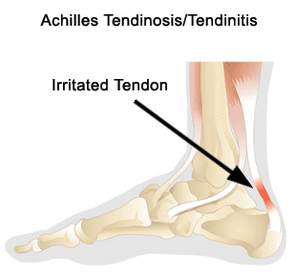
What is Achilles Tendonitis?
Achilles tendonitis may occur in athletes who over train or don't do warm-up exercises as well as in individuals who may have had a sprain or strain while working or just going for a walk. As a result of this condition one may experience an irritation and inflammation of the tendon that attaches to the back of the heel bone. Initially it can be treated with ice, rest, aspirin and anti-inflammatory medication. When the pain becomes chronic it should be professionally evaluated.